Glint is typically defined as a momentary flash of bright light, often caused by a reflection off a moving source. A typical example of glint is a momentary solar reflection from a moving car. Glare is defined as a continuous source of bright light. Glare is generally associated with stationary objects, which, due to the slow relative movement of the sun, reflect sunlight for a longer duration. The difference between glint and glare is duration. Industry-standard glare analysis tools evaluate the occurrence of glare on a minute-by minute basis; accordingly, they generally refer to solar hazards as glare.
Solar panels are designed to absorb light, and accordingly reflect only a small amount of the sunlight that falls on them when directly facing the sun compared to most other everyday objects such as grass, water and snow.
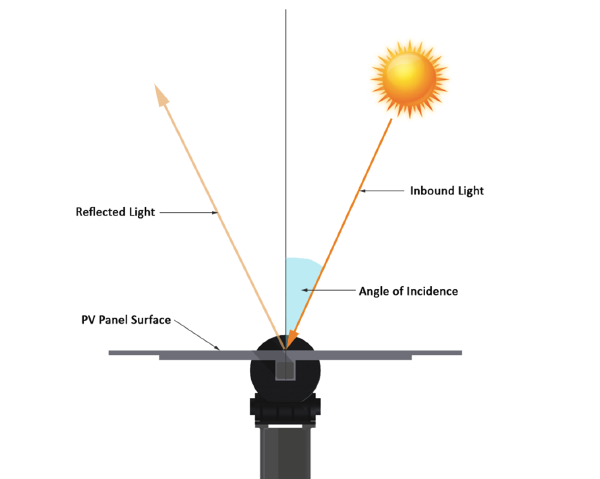
When sun is reflected on a smooth surface such as a photovoltaic surface it can result in glint (a quick reflection ) or glare which is a longer reflection for those who are on the ‘receiving’ angle. In both cases the light reflected is diminished by having first hit the surface that reflected it, unless that surface is a perfect mirror. When the sun is the original source of the light reflected off a reflective surface, the time and position at which glare or glint might occur depends on the original position of the sun in the sky in relation to the location of the viewer.
Refections from PV panels may impair observers. A key factor of reflectance is the position of PV modules relative to the sun. A panel that absorbs 90% of direct sunlight may reflect up to 60% when not directly facing the sun.